Please CLICK above to share.
In this video, I discuss:
- What Emotional Regulation is
- How “safety” is a key message
- The stress kids deal with nowadays
- What teachers are expected to do
- How to help these kids
- What’s going on with the brain and nervous system
- Fight, flight, freeze, faint
- The amygdala
Love my work and want to give? Click here!
To support me, please CLICK at the bottom to share. Click here to visit my official YouTube Channel & subscribe if you want! Thank you — Seth
Reading the transcript? Great! We’re currently uploading hundreds of transcripts so you can read them asap, but they are NOT all edited yet. This is a big process. If you notice anything wrong and want to help us, feel free to click this Google Form to share it. Thanks so much for pitching in! – Seth
Video transcript:
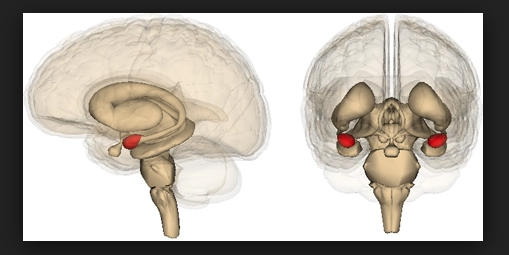
Hey, what’s up teachers? This is toughest up pro.com and I’m here to talk to you today about something called emotional regulation something that I wish that they did better training for teachers on. So I I have a picture here of the head in the heart the heart in the brain because we’re not just dealing with the brain these kids, but we’re dealing with a heart to so emotional regulation. How do kids regulate emotion? So the first thing I’m going to tell you is that a lot of kids in school as you well know are stressed out kids dealing with school nowadays are dealing with a tremendous amount of input the amount of details that they are required to manage is astounding so you guys are teachers off and get caught in the middle of it because you guys have to cram as much in and cover as much content as you can and get there is all kinds of work that is being piled upon these kids and sometimes you guys don’t have a lot of choice over how much you have to deliver while these kids are overwhelmed. No kids some kids with strong executive function deal with it very, well. Of course, a lot of the kids used to have great executive function end up being overachievers perfectionistic and end up suffering in adulthood because they have complied too much and have not learned enough about self-care, but those aren’t generally kids that I’m working with. I’m working with the kids that are struggling. I’m working with the kids with executive function problems. I’m working with the kids with ADD autism ass was dyslexia sensory integration disorder bipolar all kinds of things like that in these kids as far as executive functions concern. The details are coming at them. It’s like drinking from the firehose. They cannot manage all the details. They start falling behind about a third of the way through the semester becomes very apparent that they’re swimming Upstream the whole rest of the semester they buy middle school, they’re off and really frustrated by High School lot of them have given up on trying or figure out just how to navigate as best they can and you know, these kids are stopping. So emotional regulation though has to do with the emotions. So when they’re overwhelmed that is in emotional experience. So what happens when a kid is overwhelmed will first while sometimes visible sometimes is not a big kid is outwardly stress and you can look at them until or they’re acting out or something and you can tell that there’s a lot of stress wild and that’s fairly easy to at least identify although a lot of Kids are punished rather than supported at this time, but you can tell when kids are hourly stressed that a lot of these kids hold it in and they withdraw and they don’t have a poker face and you can’t tell that something’s going on with them, even though they’re emotionally dysregulated quite often. So what happens with emotional dysregulation is best is that the nervous system has a lot of purposes but one of the the purposes of the nervous system is to determine when there is an unsafe situation and when kids are overwhelmed by all the details there they feel unsafe even though there’s no tiger chasing them. There’s nothing unsafe going on that part of their brain doesn’t know that and I’ll explain how this works. So it’s emotional regulation. There’s a message in the brain that says, oh my gosh. We are not safe something bad’s going to happen. So what happens is this little part of the brain called the amygdala and amygdala means almond in Latin and it’s about that big. It’s a little part of the brain. Pretty small they’re about the size of an almond. And here’s the brain here are the eyeballs. Here’s the ear in the amygdala. Is this little area in the brain that they found and what they found is that the amygdala it gets a message. So here safety. We are safe. And all of a sudden the brain the senses some house and or the thought somehow since we are not safe now that could be stressed because there’s a test coming up in 5 minutes that could be stressed because there’s so much I’m working. They’re falling behind their just frustrated. They’re constantly running hot or any number of things but somehow a message is in their mind that oh my gosh. We are not safe for the nervous system needs to be able to deal with this effectively and what we do in order to deal with the lack of safety as we check with the prefrontal cortex to see if it’s realistic and of course as we know the story and a lot of kids heads and you is an adult and he is an adult we blow things out of proportion sometimes so sometimes these kids are feeling less safe than they need to be because their head is making a huge story out of it, but the brain goes in a text with usually prefrontal cortexes are we really safe? And of course in a lot of situations does no, we are not. So what happened. It sends a message to the amygdala the amygdala then says, holy crap. Something bad is going on. We need to protect ourselves know what happens is is that that part of the brain then tells the body that we need to go into fight flight freeze or faint and how does it do that? While the amygdala sends a message to the adrenal glands? What you’re located on top of the kidneys the adrenal gland send adrenalynn to the heart and the hearts then that adrenaline to the muscular system at the bicep with a fist. Okay, you like my drawing I’ve been practicing his drawing for a long time. It’s getting better. Huh. So the amygdala says the brain says, we’re not safe. Okay, cool. I got this. All right, I’ll send a message to the adrenals. The adrenal say, oh, we’re not safe. Okay, we’ll send adrenaline to the heart. The heart is all we’re not say poke will send them into the muscular system. That way we can fight flight freeze or faint in order to ensure our safety, but the child is sitting in a classroom and they are perfectly safe. They’re having Emotional experience they are now emotionally dysregulated. Do you think they’re going to be able to focus and concentrate in class? They’re emotionally dysregulated if they got screamed at by their parents in the morning or they had a great experience with their parents in the morning and then they got into class and they got yelled at by teacher or they perceive they got yelled at or their bullied or they’re just sad and depressed and lonely or they’re angry or anxious. Who knows what’s going on. But either way if they are in a classroom and they are emotionally dysregulated their prefrontal cortex is not in a learning mode. They’re going to try to be learning in in class as much as they can. But if you imagine that it’s like a whole bunch of filters in Den not lot of learning is getting through those filters then that it because they’re emotionally dysregulated that is obviously interfering now. What can you do to help kids who are emotionally dysregulated, how can you help kids to regulate emotion while breathwork meditation something called co-regulation where use the adults? Model your own regulation help them just by modeling it and and then any number of ways, but I’m not going to get into too much of that on this video, but I will say this this is my opinion. But the number one most important thing schools going to be starting a couple weeks to do in any classroom is to get kids to know that they are emotionally safe and to me it takes four to six weeks our kids to really get to know, you know that they’re emotionally safe so that building of emotional safety in the beginning of school. So critical and some teachers do it some teachers don’t do it some teachers feel a lot of pressure to dive straight into curriculum cuz you just got out of training then you have so much to cover your so overwhelmed and some teachers really really focus on spending that time building that emotional regulation building. Safe environment in the classroom to me is the number one biggest priority at the beginning of the year because that will set the tone for the whole rest of the year the safer they feel in your class the more Going to be able to learn throughout the year, and he had just want to do a quick video on that. I hope you like it. Please comment below and tell me what you think teachers. Tell me what videos you want. Tell me what you think of this. Tell me what you need to know about emotional regulation. How can I help you? All right. I hope you have a great school year take.